PSY2043 Ch02 Lecture Notes
PSY2043 Introduction to Psychology
Ch02 Biological Foundations of Psychology
INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES
- Understand the organization and the physiology of the human brain.
- Have learned the research methods used to study the brain.
- computerized axial tomography (CT)
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- positron emission tomography (PET)
- Be able to consider evolutionary arguments.
- Darwin – Nature selection – variations on inheritable traits that most contribute to an organism’s survival that are passed on to the next generation.
- Explain the basics of the biology of the brain.
- Identify key areas in the human brain, including their function.
- Understand key principles concerning the heredity of behavior.
- An individual’s hereditary potential, which is transmitted by the chromosomes and genes, influences his or her psychological and physical characteristics.
The Study of the Biological Bases of Psychology
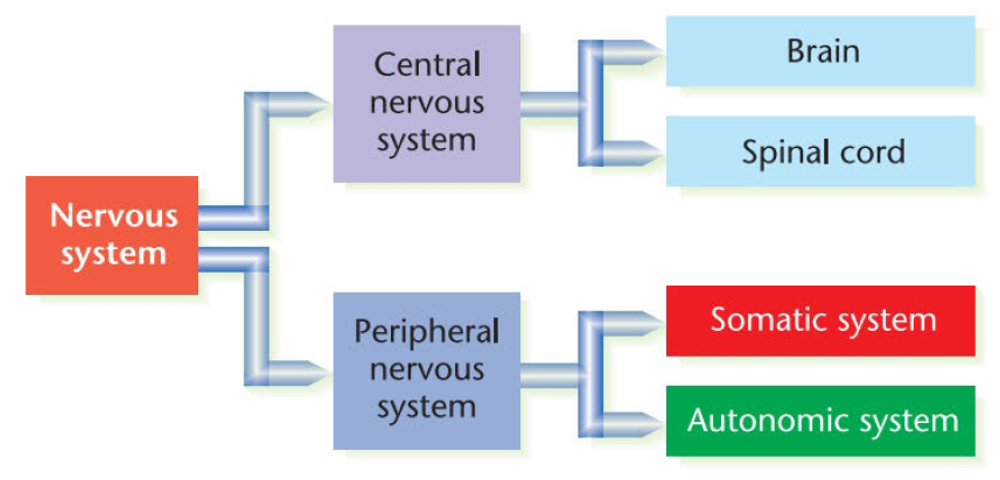
- peripheral nervous system 周围神经系统
- spinal cord 脊柱
- afferent nerves 传入神经
- efferent nerves 传出神经
- somatic nervous system 躯体神经系统
- autonomic nervous system 自主神经系统
Neurons, the Building Block of the Nervous System
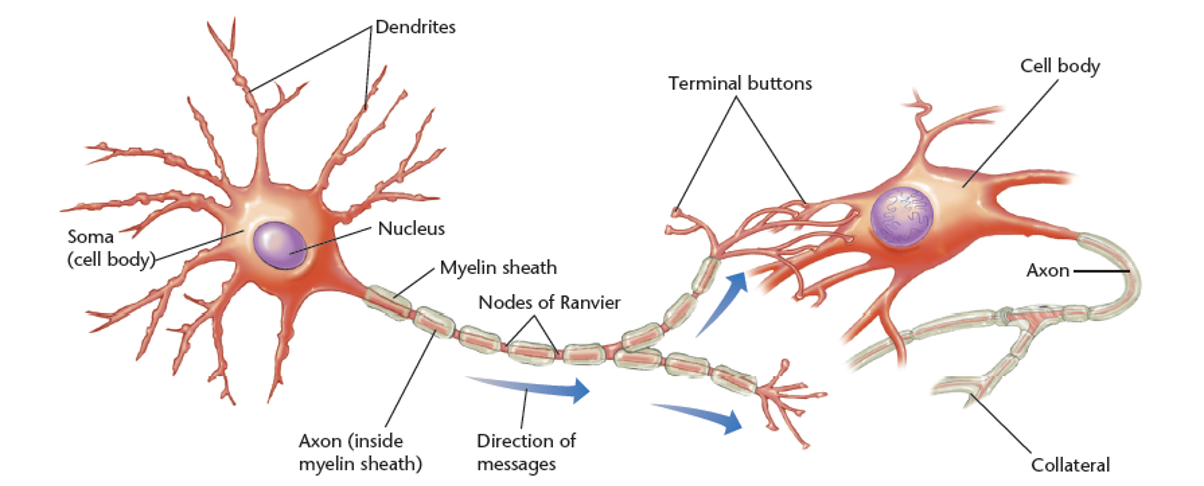
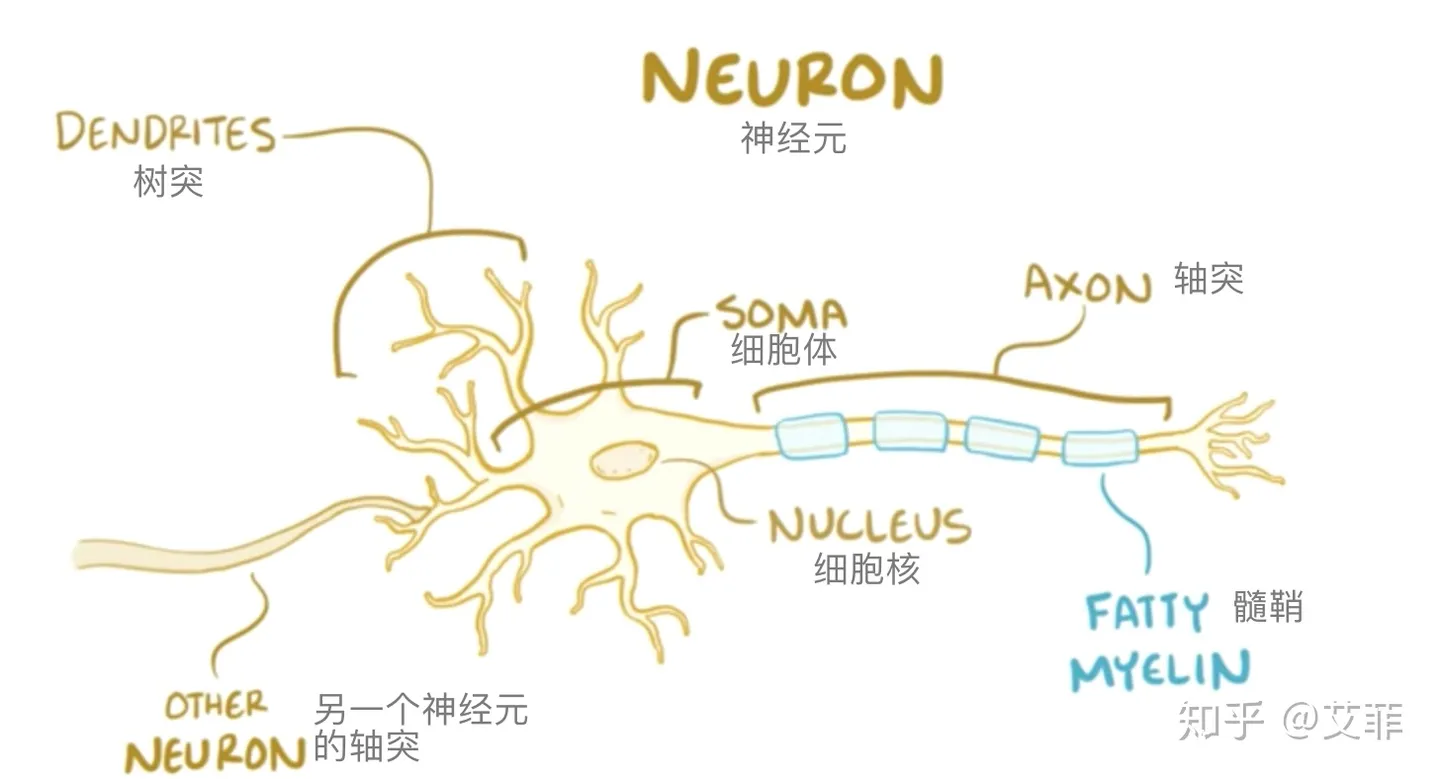
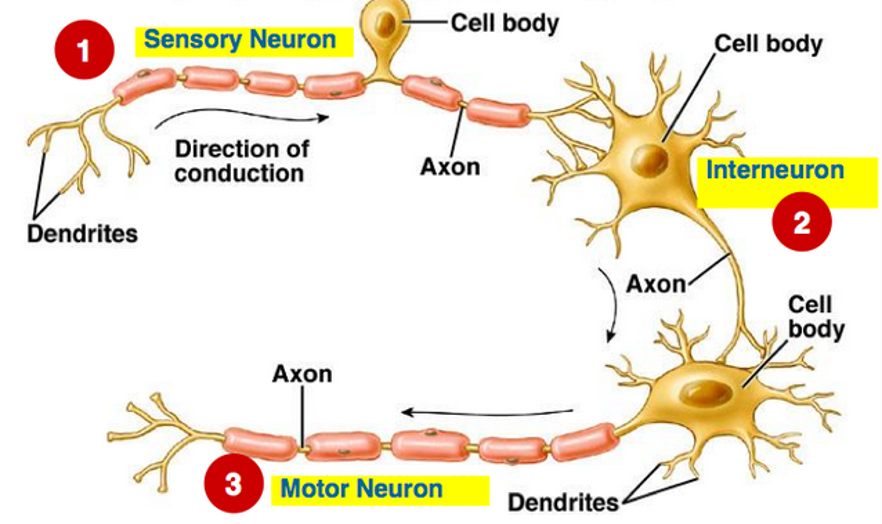
- Neurons’ three categories
- Sensory neurons – transmit impulses from receptors to CNS
- Motor neurons – carry outgoing signals from CNS to muscles and glands
- Inter-neurons – connect sensory and motor neurons
Action potentials
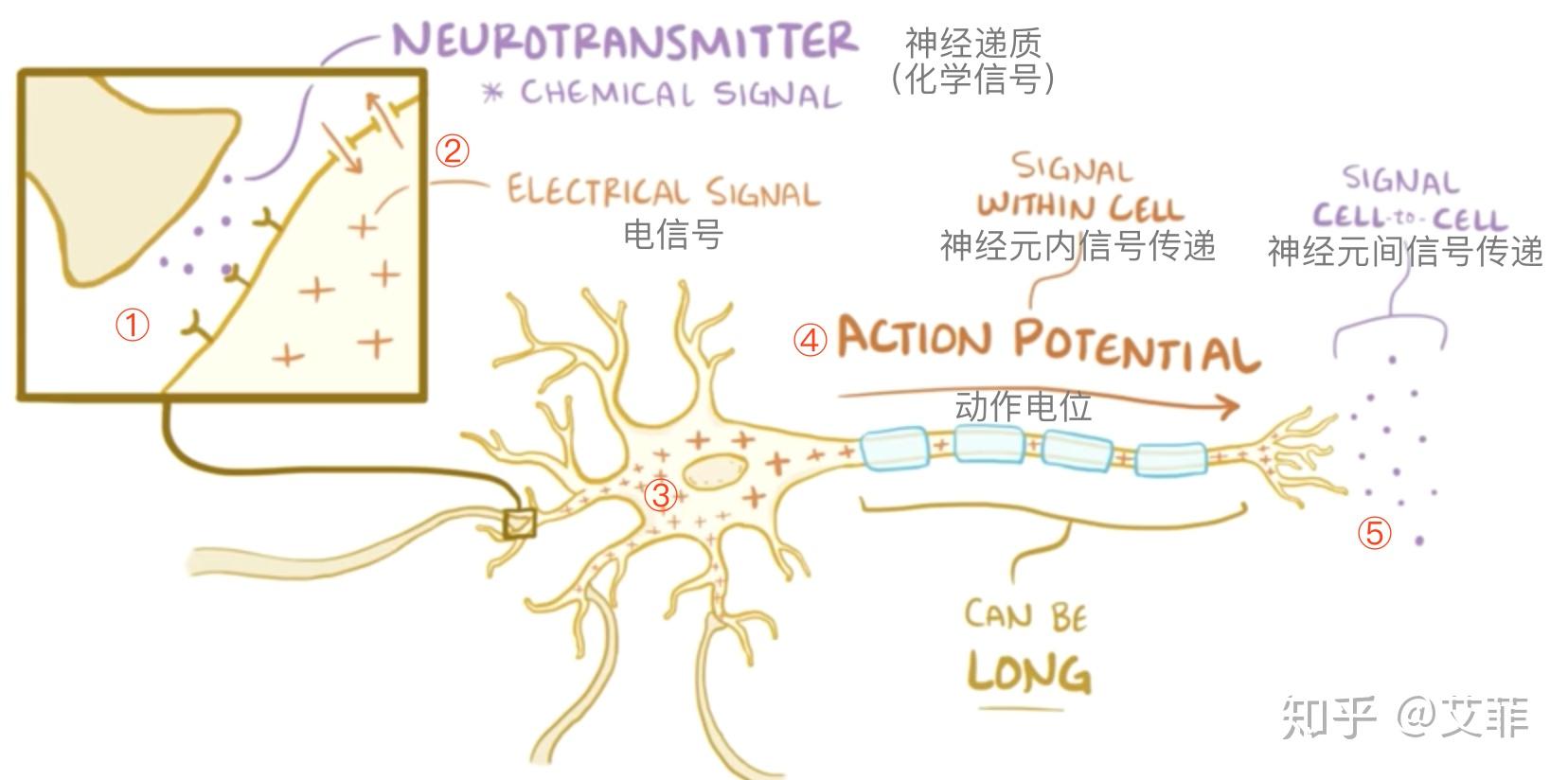
5分钟极速认识神经系统和脑 - 艾菲的文章 - 知乎
神经信号的传递步骤:(看图理解会更快哦~)
- 前一个神经元的轴突末端,释放化学信号(神经递质),通过突触(前后两个神经元接触的结构),传递至后一个神经元的树突前端的位置;
- 树突前端的膜打开一道门,接收神经递质携带的信号并产生正负离子交换,在细胞内积累对应电极的离子;
- 多个树突接收的信号共同形成细胞整体的电信号并达到兴奋临界点时,激发电信号(动作电位);
- 电信号通过轴突跳跃式快速传递至末端;
- 电信号转化为化学物质,再继续传下去;
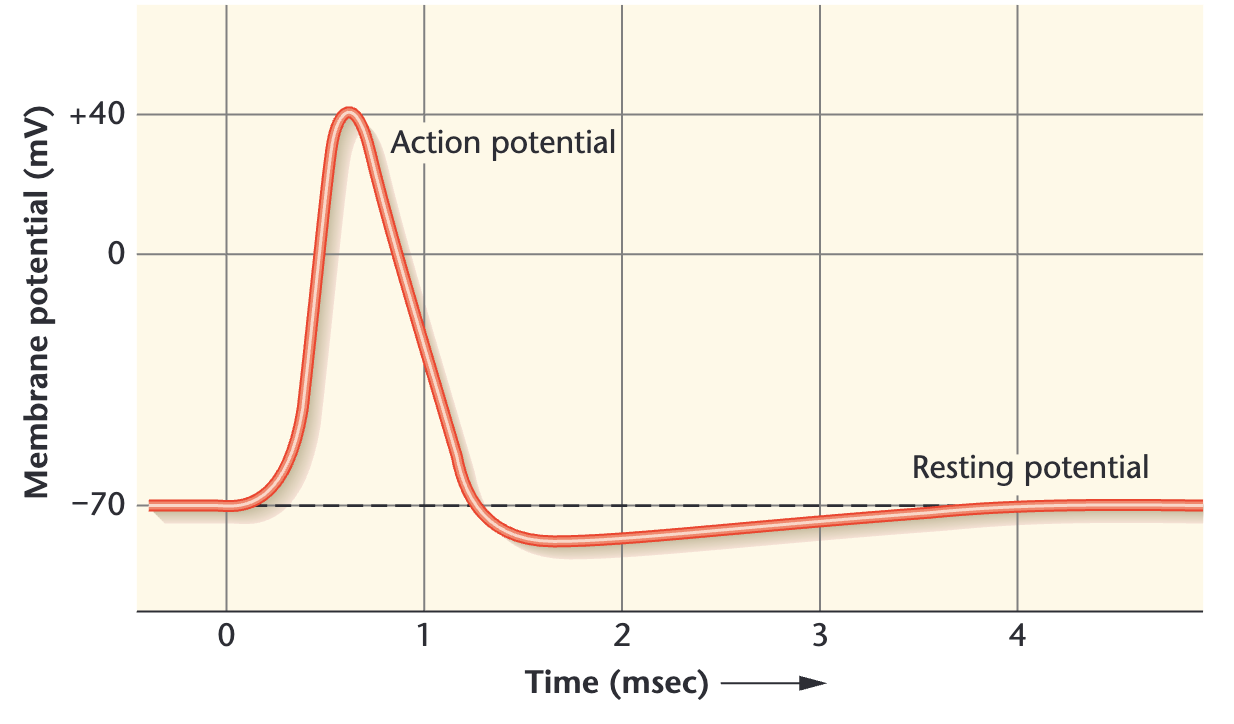
高中生物静息电位和动作电位 - 朝济夕设版的朝夕的文章 - 知乎
- 静息电位(K+ 的平衡电位)
- 产生条件
- 细胞膜内外离子分布不平衡
- 就正离子来说,膜内 K+ 浓度较高,约为膜外的30倍。膜外 Na+ 浓度较高约为膜内的10倍。从负离子来看,膜外以Cl-为主,膜内则以大分子有机负离子 (A-) 为主。
- 膜对离子通透性的选择
- 在静息状态下,膜对 K+ 的通透性大,对 Na+ 的通透性则很小(Na+ 通道关闭),对膜内大分子 A- 则无通透性。
- 产生过程
- K+ 顺浓度差向膜外扩散,膜内 A- 因不能透过细胞膜被阻止在膜内。致使膜外正电荷增多,电位变正,膜内负电荷相对增多,电位变负,这样膜内外便形成一个电位差。
- 当促使 K+ 外流的浓度差和阻止 K+ 外流的电位差这两种拮抗力量达到平衡时,使膜内外的电位差保持一个稳定状态,即静息电位。
- 动作电位
- 产生条件
- 细胞膜内外离子分布不平衡。细胞内外存在着Na+浓度差,Na+在细胞外的浓度是细胞内的13倍之多。
- 膜对离子通透性的选择。细胞受到一定刺激时,膜对Na+的通透性增加。
- 产生过程
- 去极化
- 细胞受到阀上刺激→细胞外Na+顺浓度梯度流人细胞内→当膜内负电位减小到阈电位时Na+通道全部开放→Na+顺浓度梯度瞬间大量内流(正反馈倍增)→细胞内正电荷增加→膜内负电位从减小到消失,进而出现膜内正电位→膜内正电位增大到足以对抗由浓度差所致的Na+内流→膜两侧电位达到一个新的平衡点。该过程主要是Na+内流形成的平衡电位,可表示为动作电位模式图的上升支。
- 复极化
- 达峰值时Na+通道迅速关闭而失活→Na+内流停止→K+通道被激活→膜对K+的通透性增加→K+借助于浓度差和电位差快速外流→膜内电位迅速下降(负值迅速上升)→电位恢复静息值。该过程是K+外流形成的,可表示为动作电位模式图的下降支。
- Na+-K+ 泵转运
- 当膜复极化结束后,有一部分Na+在去极化中扩散到细胞内,一部分K+在复极过程中扩散到细胞外。这样细胞膜上Na+-K+泵就会被激活,并主动将膜内的Na+泵出膜外,同时把流失到膜外的K+泵回膜内,以恢复兴奋前的离子分布的浓度
Synaptic transmission and neural coding
Neurotransmitters
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
- GABA – Major inhibitory neurotransmitter in brain. Drugs that alleviate anxiety enhance activity of GABA.
- Serotonin – Important in mood and social behavior. Drugs that alleviate depression and anxiety increase serotonin levels in synapse.
Excitatory neurotransmitters
- Acetylcholine – Involved in memory and attention; decreases associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Also transmits signals between nerve and muscle.
- Norepinephrine – Increased by psycho-timulants. Low levels contribute to depression.
- Dopamine – Mediates the effects of natural rewards (food and sex, for example) and drugs of abuse.
- Glutamate – Major excitatory neurotransmitter in brain. Involved in learning and memory.
The Organization of the Brain
- Categories
- Location
- the hindbrain
- the midbrain
- the fore brain
- Function (McLean’s three concentric layer)
- the central core(brainstem) – regulates our most primitive behaviors
- the limbic system – controls our emotions
- the cerebrum – regulates our higher intellectual processes
- Location
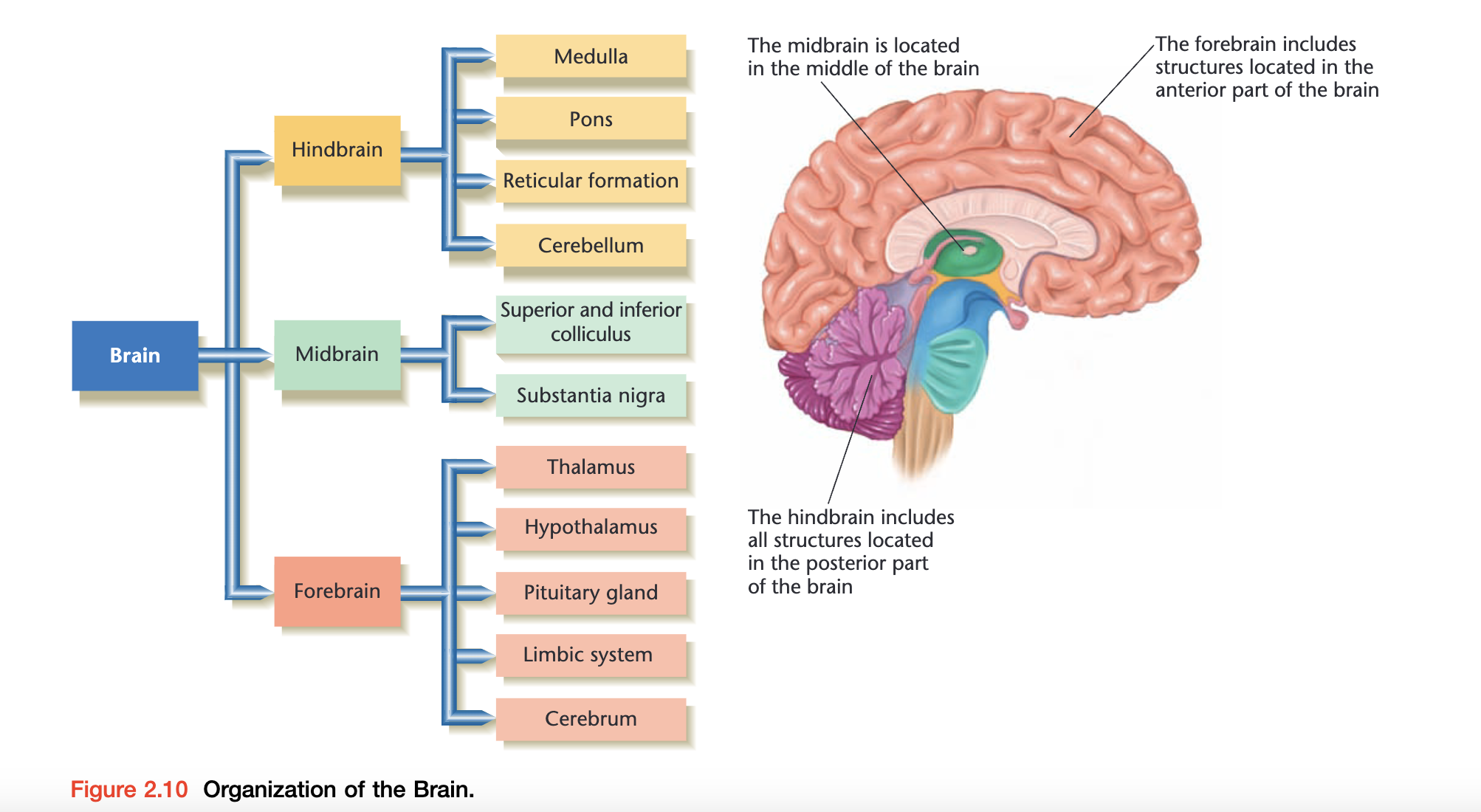
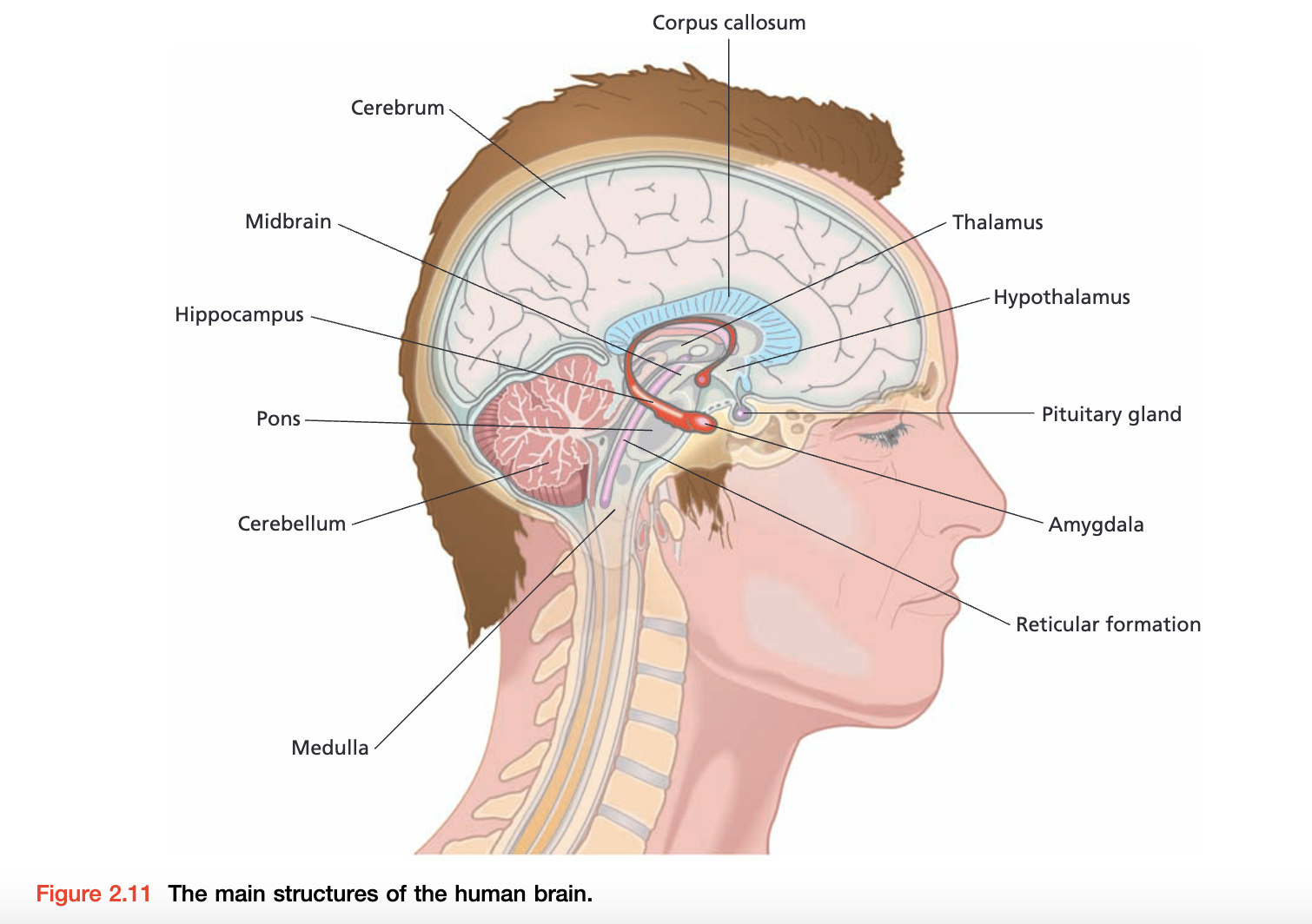
The hindbrain
- Medulla 髓质 – 一个狭窄的结构,控制呼吸和一些反射,有助于保持直立姿势
- Pons 脑桥 – 对控制注意力和睡眠时间非常重要
- Reticular formation 网状结构 – control arousal
- Cerebellum 小脑 – 动作的协调
The midbrain
- Superior and inferior colliculus 上丘和下丘 – 对于向大脑传递感觉信息和控制运动(包括眼球运动)非常重要
- Substantia nigra 黑质 – 多巴胺通路(又称 “奖赏通路”)的重要组成部分
The forebrain
- Thalamus 丘脑 – 充当感觉中继站,将感官感受器(如视觉和听觉)传入的信息导向大脑
- Hypothalamus 下丘脑 – 下丘脑中的中枢调节饮食和性行为。下丘脑通过控制自主神经系统来维持体内平衡(Homeostasis 稳态)
- Pituitary gland 垂体 – 影响激素的产生
- Limbic system
- Hippocampus – memory
- Amygdala - emotional
- Cerebrum
- Cerebral cortex – the out layer of cerebrum
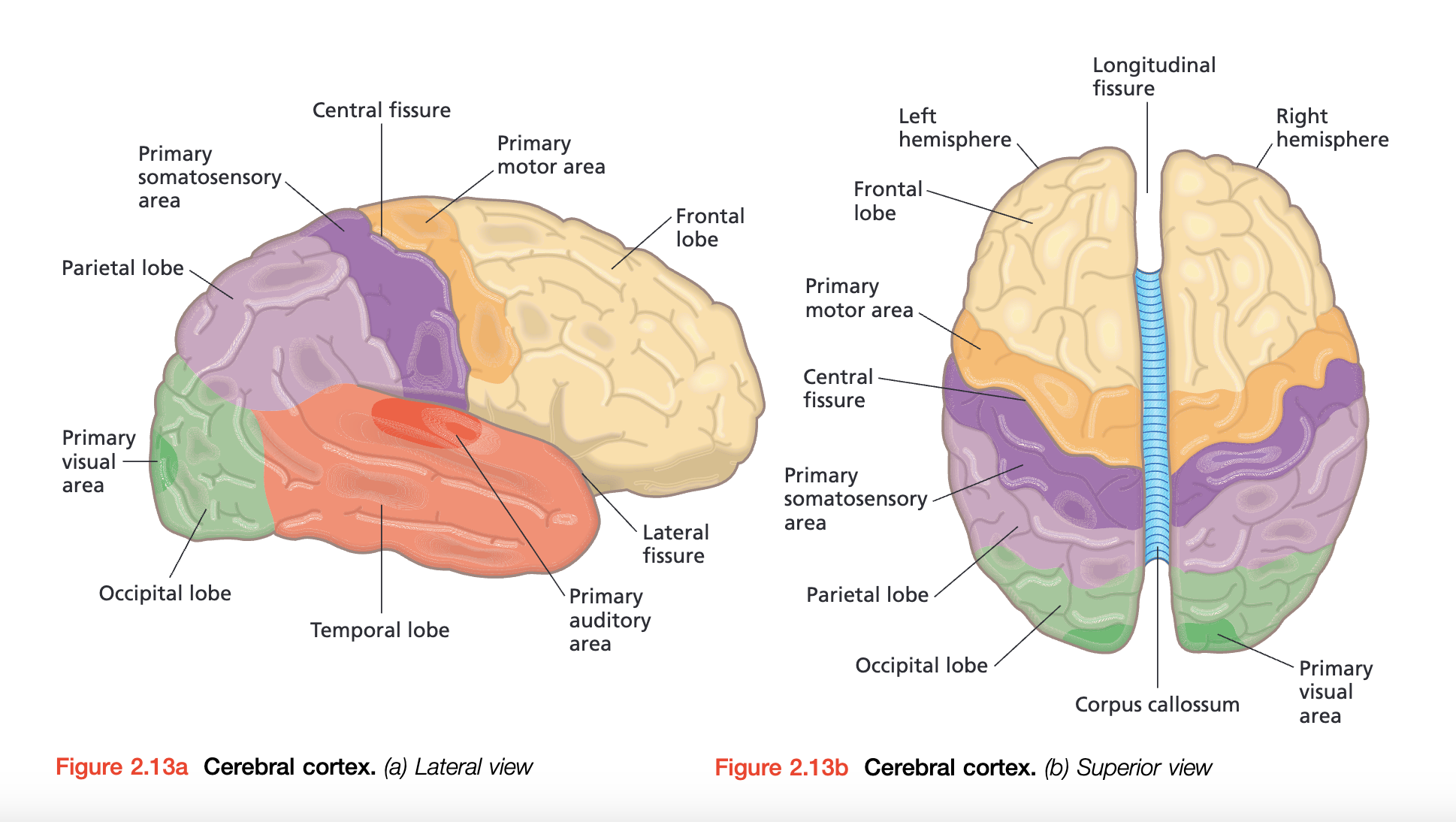
- left and right hemispheres 左右大脑半球
- 每个 hemisphere 可以被分为 4 个 lobes
- Frontal lobe 额叶
- Parietal lobe 顶叶
- Occipital lobe 枕叶
- Temporal lobe 颞叶
- Central fissure 分割额叶和顶叶
- Lateral fissure 分割颞叶和其他叶
- 每个 hemisphere 可以被分为 4 个 lobes
- longitudinal fissure 纵裂 脑裂 – 分割 hemispheres
- corpus callosum 胼胝体 – 连接大脑皮层的 hemispheres
- Cerebral cortex – the out layer of cerebrum
Mapping the brain
Asymmetires in the brain
- Language
- aphasia 失语症 – 无法产生语言
- Broca’s area – 左半球额叶
- receptive aphasia 接受性失语症 – 无法理解语言
- Wernicke’s area – 左半球颞叶
- aphasia 失语症 – 无法产生语言
- Split-Brain research – 切断胼胝体会导致两个半球功能上的显著差异
- Hemispheric specialization 半球专门化
- Left hemisphere – 擅长语言和数学能力
- Right hemisphere – 可以理解一些语言,但不能通过言语交流;它具有高度发达的空间和模式感。
The Autonomic Nervous System
- Autonomic nervous system
- Sympathetic nervous system – active during excitement
- Parasympathetic nervous system – dominant during quiescence
The Endocrine System
Evolution, Genes, and Behavior
Evolution of behavior
- Ultimate causes – help us to understand why a behavior exists in the first place
- Proximate causes – explain how a behavior is generated
Chromosomes and genes
Genetic studies of behavior
PSY2043 Ch02 Lecture Notes
